Type a keyword into the search bar, hit enter, click one of the 10 blue links and land on the website you were looking for: this is how users have been searching the internet for years – and SEO experts have optimized websites accordingly. Then came AI chatbots, and started answering user questions directly. Google’s AI Overviews in particular are leading to significantly fewer clicks on search results. To stay visible, SEO needs reinforcement: GEO. Generative Engine Optimization ensures that brands appear within the answers provided by generative AI.
The times are changing: SEO needs a boost
It used to be simple: if you wanted to be found online, you optimized your content for Google. But today, Google Search faces real competition. Many users no longer start their research with a classic search query but by asking ChatGPT or another AI chatbot. Overall, the trend is clear: users want quick answers from AI, without having to click on a link or spend time on lengthy research.
Google isn’t taking this threat to its search monopoly lying down, of course. Since March 2025, the search giant’s AI Overviews have been available in German-speaking countries. These AIOs provide users with instant answers — not just a list of blue links. This ensures that Google remains the go-to destination for information.
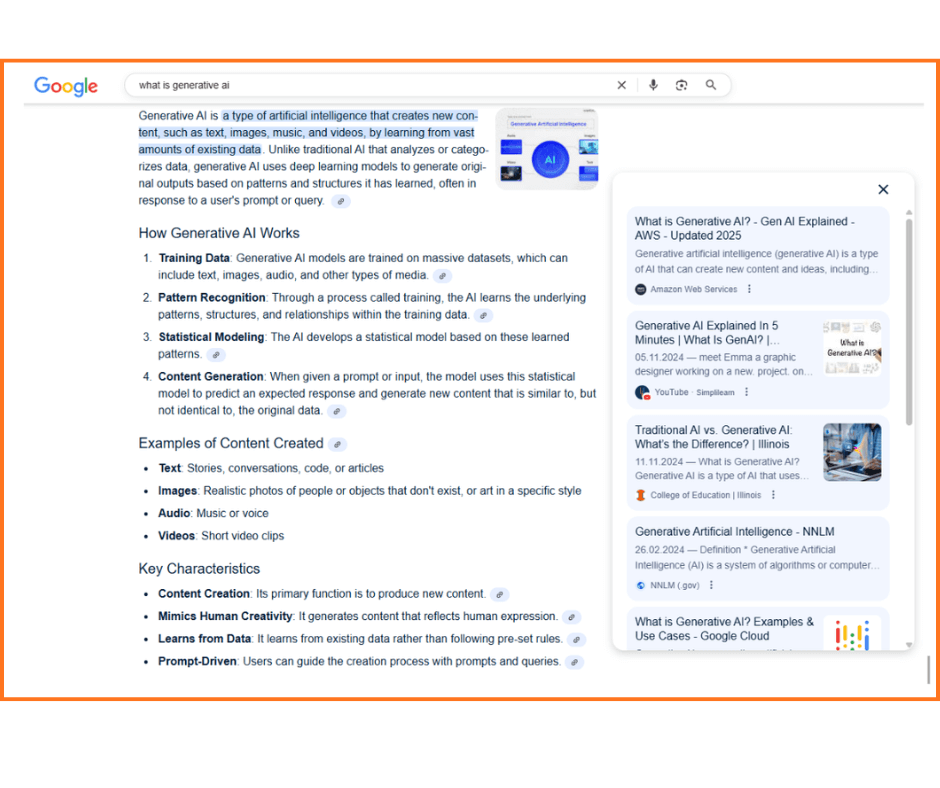
Google also announced that it would transition to its own “AI Mode,” gradually replacing the familiar 10 blue links with AI-generated answers. The introduction of featured snippets back in 2014 was Google’s first step away from being a pure search engine toward becoming an answer engine. With AI Overviews, this evolution continues. Instead of quoting snippets of text, AIOs now generate complex, AI-created responses to specific questions.
This shift is reshaping the customer journey. Many users no longer scroll to the traditional search results below. For companies, that means rethinking online visibility. Websites now need to be optimized not only for search engines, but for generative AI as well.
That doesn’t mean SEO or classic Google Search are dead. In fact, Google Search grew by more than 20% in 2024, and Google recorded about 373 times as many search queries as ChatGPT. But to future-proof your brand, brands should pair SEO with GEO—ensuring visibility both in traditional search results and AI-generated answers.
What exactly is GEO?
GEO stands for “Generative Engine Optimization”—the optimization of websites so they appear in the answers of generative AI systems. Other terms such as AEO (Answer Engine Optimization) or LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization) are also sometimes used to describe optimization for AI.
While traditional Search Engine Optimization (SEO) aims to achieve top rankings in organic search results, GEO focuses on how content is processed and displayed within the outputs of chatbots, AI assistants, and AI-generated responses to search queries.
The goal of GEO is to make sure your company or brand appears in the responses of generative AI—either as a cited source or through a brand mention. To achieve this, content must be structured in a way that AI systems can understand it, consider it quotable, and include it in their outputs.
How does GEO work?
Generative AI such as ChatGPT is either a training-based system (e.g., Claude, Llama), a search-based system (e.g., Google AI Overviews, Perplexity), or a hybrid system (e.g., ChatGPT Search, Gemini). Systems that rely solely on their training data are difficult to influence. However, models that use external sources (e.g., search engines) offer the opportunity to increase visibility in AI-generated responses.
For example, when ChatGPT is asked, “What is SEO?”, it searches its training data, i.e., its internal knowledge database (Figure 2). When it comes to “encyclopedic” or factual knowledge, chatbots usually rely on their training data, so publishers have little opportunity to generate traffic from them.

The situation is different for more complex or up-to-date information. When asked about GEO agencies in Vienna, for example, the chatbot provides a list of agencies including sources or websites. In this case, it searched the internet for up-to-date information (Figure 3).

Similarly, AI Overviews use Google’s search index to retrieve up-to-date information. In the background, the AI breaks down the user’s specific query into several related search queries (“fan-out”), retrieves the best results of these search queries, and summarizes them concisely.
For example, an AI system could break down the user’s question “How does AI influence online marketing?” into the following sub-questions to better understand the topic:
- Advantages of AI in marketing
- Risks of AI in marketing
- AI tools for advertisers
- Examples of successful AI campaigns
The only question is: Which content is referenced by AI, and why?
Only content that Google has already rated as trustworthy, relevant, and high-quality makes it onto the shortlist for AI Overviews. So, it all comes down to E-E-A-T signals. Expert articles, studies, certificates, mentions on industry platforms, author profiles listing qualifications, as well as reviews and reputation in professional directories increase the chances of being cited as a reference in generative AI.
ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity most frequently cite earned media—i.e., organic mentions or recommendations from third-party sources.
In addition, a clear website structure and well-organized content with easily extractable information (clear headings, FAQ structures, bullet points) are helpful. Pages with predominantly promotional content and little real value, on the other hand, tend to be ignored.
In-depth, well-researched content is more likely to appear in AI-generated answers. The more perspectives a website covers on a given topic, the higher the chance that it will achieve a good ranking in the fan-out queries running in the background, and thus be considered a credible source.
Of course, a clean technical implementation is also essential to ensure that the content is easily accessible for LLM crawlers.
In short: we cannot directly influence LLM training data, but we can influence the external sources generative AI uses—and that’s where we want to increase our visibility. This means, for example, that a good Google ranking increases the chances of being mentioned by Gemini or in AI Overviews (and the same applies, of course, to good Bing rankings for ChatGPT).
Therefore, SEO is a key factor for gaining visibility in generative AI responses.
In that sense, SEO is the foundation on which GEO is built. While SEO focuses on improving rankings in search engines to increase visibility and drive traffic, GEO takes it a step further by ensuring that content is understood, cited, and considered trustworthy by AI systems.
From clicks to impressions and from keywords to questions
Generative AI is changing search behavior: users are clicking less because AI provides the answer directly. In the blog article AI Overviews Are Reshaping the Customer Journey: Can SEO Keep Up? our CEO Thomas Kloos takes a closer look at this phenomenon.
This shift is also bringing about a change in search queries. Instead of short keywords such as “seo agency vienna,” users now tend to use long-tail keywords or even ask longer and more specific questions such as “Which SEO agencies in Vienna have experience in e-commerce?” Unlike SEO, therefore, GEO focuses on prompts —that is, full questions..
This change also comes with a new set of new expectations: instead of doing their own research and piecing together information from multiple sources, users now expect ChatGPT or AI Overviews to deliver complete answers, recommendations and context right away.
The success of SEO can be measured by rankings on search engine results pages, the resulting clicks, the traffic generated on the website, and the conversions attributed to this channel. At GEO, this works a little differently: as clicks decline, success is measured by visibility within AI-generated responses—in other words, whether and how often your own brand, products, or content are cited or mentioned by ChatGPT, Gemini, or Perplexity.
Today, it is no longer “just” about visibility in rankings, but about visibility through helpful and trustworthy answers.
We explain how we measure this new kind of visibility in our blog article on visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity and Google AI Overviews.
Our recommendation: SEO + GEO
Should you invest in GEO?
Yes, definitely!
Click-through rates have dropped significantly since the introduction of AIOs—early studies report losses of more than 50%. A report by the Pew Research Center found that only about 8% of users click on classic website links when AIOs are displayed for a search query, compared to about 15% when they are not.
And we are only at the beginning of AI’s evolution and integration. The trend is clear: established search engines like Google and Bing are continuously adding new AI features to their products. Leading players such as OpenAI, Perplexity, and Anthropic regularly release new, even more powerful models. And emerging competitors are surprising us with innovative applications. AI is set to play a defining role in shaping the future of digital marketing.
Strong rankings on Google or Bing are still essential for content to even make it into the data pool of generative systems. GEO then takes it further by making sure that this content is recognized by AI systems as relevant, trustworthy, and quotable.
Want to know how a GEO project works at our agency and what services we offer? You can find out here!
Quellen
1: https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2025/07/22/google-users-are-less-likely-to-click-on-links-when-an-ai-summary-appears-in-the-results/